Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of Information and Communication Technology (ICT), Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT has proven Singapore as emerging as a shining beacon of growth and innovation over the past decade. This dynamic city-state, nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, has made remarkable strides in establishing itself as a global ICT hub. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the multifaceted journey of Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT, exploring the factors that have fueled its growth, the challenges it has overcome, and the promising future that lies ahead.
Infographics by GO-Globe Singapore
Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT Powerhouse
Singapore's ascent to becoming a global ICT hub has been nothing short of remarkable. This journey can be divided into several key phases that have collectively shaped its current status:
Early Infrastructure Development
Singapore's commitment to infrastructure development played a pivotal role in Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT . The nation invested heavily in building a robust telecommunications network, with state-of-the-art data centers, undersea cables, and cutting-edge technology infrastructure. This solid foundation laid the groundwork for future advancements.
Government Initiatives and Policies
One of the most significant drivers of Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT has been the government's unwavering support and strategic policies. Initiatives like the "Smart Nation" program, which focuses on harnessing technology for societal advancement, have attracted both local and international tech giants.
Attracting Global Talent
Singapore's pro-business environment and progressive immigration policies have attracted top tech talent from around the world. The city's vibrant ecosystem fosters innovation and collaboration, creating a fertile ground for startups and multinational corporations alike. Top talent has been drawn to Singapore in a variety of industries, including blockchain technology, cybersecurity, data analytics, and software development. These skills support the development and innovation of Singapore's ICT sector.
Research and Development
The commitment to research and development (R&D) has been a cornerstone of Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT. Investment in R&D centers, collaboration with universities, and partnerships with industry leaders have led to groundbreaking innovations.
Transformative Technologies
The growth of Singapore's ICT sector has been closely intertwined with the rapid development of transformative technologies. Here are some key areas where Singapore has made significant strides:
5G Revolution
Singapore was among the early adopters of 5G technology, which promises ultra-fast connectivity and low latency. This leap in telecommunications infrastructure has paved the way for innovations in IoT, autonomous vehicles, and telemedicine which resulted in Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The city-state has embraced AI across various sectors, from healthcare and finance to logistics and manufacturing. AI-powered solutions are enhancing productivity and efficiency while driving economic growth.
Fintech Hub
Singapore has emerged as a leading fintech hub, with a thriving ecosystem of startups and established financial institutions. The city's supportive regulatory environment has encouraged experimentation and innovation in the financial sector.
Cybersecurity Leadership
As the digital landscape expands, so does the importance of cybersecurity. Singapore has positioned itself as a global leader in cybersecurity, with a robust framework to protect critical infrastructure and digital assets.
Singapore as a Global Hub in the ICT Sector: Facts, Figures and Latest Statistics
-
Government Investment in ICT
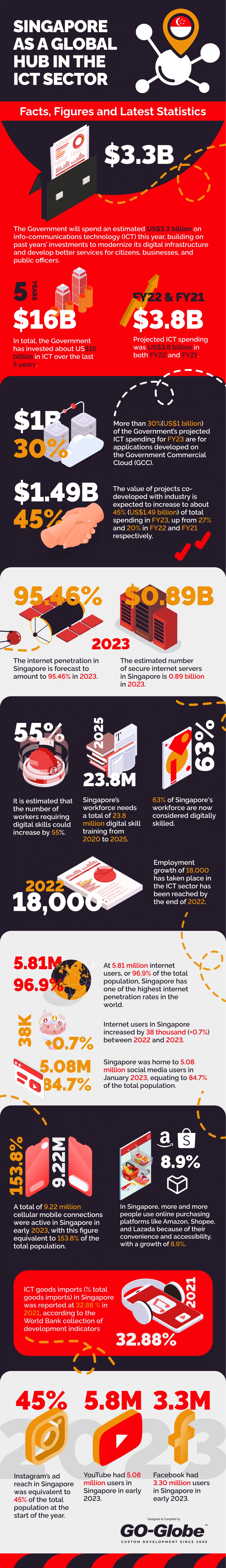
- Estimated ICT Spending for FY24: The government will spend an estimated US$3.3 billion on ICT this year, building on past years’ investments to modernize its digital infrastructure and develop better services for citizens, businesses, and public officers.
- Total ICT Investment Over 5 Years: The government has invested approximately US$16 billion in ICT over the last five years.
- Projected ICT Spending for FY22 and FY21: Projected ICT spending was US$3.8 billion for both fiscal years 2022 and 2021.
- Government Commercial Cloud (GCC): More than 30% (US$1 billion) of the government's projected ICT spending for FY23 is allocated for applications developed on the GCC.
- Industry Co-developed Projects: The value of projects co-developed with industry is expected to increase to about 45% (US$1.49 billion) of total spending in FY23, up from 27% in FY22 and 20% in FY21.
Internet and Mobile Connectivity
- Internet Penetration: As Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT , Internet penetration in Singapore has reached 89% in 2024.
- Secure Internet Servers: The estimated number of secure internet servers in Singapore is 0.89 billion in 2023.
- Internet Users: At 5.81 million internet users, or 96.9% of the total population, Singapore has one of the highest internet penetration rates in the world.
- Increase in Internet Users: Internet users in Singapore increased by 38 thousand (+0.7%) between 2022 and 2023.
- Social Media Users: Singapore was home to 5.08 million social media users in January 2023, equating to 84.7% of the total population.
- Cellular Mobile Connections: A total of 9.22 million cellular mobile connections were active in Singapore in early 2023, equivalent to 153.8% of the total population.
Employment and Digital Skills
- Digital Skills Demand: It is estimated that the number of workers requiring digital skills could increase by 55%.
- Total Digital Skill Training Needed: Singapore’s workforce needs a total of 23.8 million digital skill training sessions from 2020 to 2025.
- Digitally Skilled Workforce: 63% of Singapore's workforce are now considered digitally skilled.
- Employment Growth in ICT: Employment growth of 18,000 in the ICT sector was reached by the end of 2022.
E-commerce and Online Activity
- Growth in Online Purchasing: More people are using online purchasing platforms like Amazon, Shopee, and Lazada due to their convenience and accessibility, with a growth of 8.9%.
- ICT Goods Imports: ICT goods imports accounted for 32.88% of total goods imports in Singapore in 2021, according to the World Bank.
For more Information : E-Commerce In Singapore – Statistics And Trends
Social Media and Digital Advertising
- Instagram Ad Reach: Instagram’s ad reach in Singapore was equivalent to 45% of the total population at the start of the year.
- YouTube Users: YouTube had 5.08 million users in Singapore in early 2023.
- Facebook Users: Facebook had 3.30 million users in Singapore in early 2023.
Challenges Faced and Overcome
While the growth of Singapore as an ICT hub has been impressive, it hasn't been without its challenges. Over the past decade, the city-state has encountered and successfully navigated several obstacles:
Talent Shortage
The demand for tech talent has sometimes outstripped supply. However, Singapore's proactive approach to talent development, including scholarship programs and skills training, has helped bridge this gap.
Cybersecurity Threats
As the ICT sector grows, so does the risk of cyber threats. Singapore has proactively addressed this challenge through stringent regulations, public-private partnerships, and investments in cybersecurity infrastructure.
Competition from Global Hubs
Singapore faces competition from other global ICT hubs like Silicon Valley, Shanghai, and Bangalore. However, its strategic location, political stability, and robust legal framework continue to attract businesses and investors.
The Future: A Bright Horizon
The trajectory of Growth of Singapore as a Global ICT hub remains highly promising. Several factors point towards a bright future:
Emerging Technologies
Singapore is poised to lead in emerging technologies such as quantum computing, blockchain, and biotechnology. Investments in research and innovation will continue to drive growth. The ICT sectors of Singapore, such as software development, data analytics, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology, have experienced tremendous growth. These sectors have drawn top talent from around the world, helping to cement Singapore's status as a major ICT powerhouse.
International Collaboration
The city-state's commitment to international collaboration and partnerships will facilitate knowledge exchange and promote cross-border innovation. Major tech events like the Singapore FinTech Festival and the Singapore International Cyber Week have been held in Singapore, highlighting the growth of the ICT industry in this sector. Industry executives, creators, and investors from all around the world congregate at these events.
Sustainability
Singapore is committed to sustainable ICT growth, with initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and adopting green technologies.
Resilience
The COVID-19 pandemic showcased Singapore's resilience and adaptability. The ICT sector played a crucial role in enabling remote work and digital services, further emphasizing its importance.
Conclusion
The growth of Singapore as a global ICT hub in the past decade is a testament to its vision, resilience, and commitment to innovation. With a strong foundation, a focus on transformative technologies, and a bright future ahead, Singapore continues to be a beacon of ICT excellence on the world stage. As technology evolves, Singapore remains at the forefront, ready to embrace the challenges and opportunities of the digital age.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: How has Singapore attracted global tech talent?
A: Singapore's pro-business environment, favorable immigration policies, and a vibrant tech ecosystem have been key factors in attracting global tech talent.
Q2: What is the "Smart Nation" program?
A: The "Smart Nation" program is a government initiative focused on leveraging technology for the betterment of society, promoting digital innovation across various sectors.
Q3: How has Singapore addressed the challenge of cybersecurity?
A: Singapore has addressed cybersecurity challenges through stringent regulations, public-private partnerships, and significant investments in cybersecurity infrastructure.
Q4: What are some emerging technologies Singapore is investing in?
A: Singapore is investing in emerging technologies such as quantum computing, blockchain, and biotechnology to stay at the forefront of innovation.
Q5: How did Singapore adapt to the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic?
A: Singapore's ICT sector played a crucial role in enabling remote work and digital services, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
Q6: What is the significance of Singapore's location in its ICT growth?
A: Singapore's strategic location at the crossroads of global trade routes has been instrumental in attracting businesses and investors to its ICT sector.