Singapore uncertain outlook amid inflation, future challenges and growth potential in 2024
Singapore, a global financial hub and bustling city-state, has been navigating its way through various economic challenges over the years. As we look into the future, it's essential to analyze the uncertain outlook amid inflation, future challenges, and growth potential in 2024. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of Singapore's economic landscape, including the factors influencing its growth, the challenges it faces, and the potential opportunities on the horizon.
Infographics by GO-Globe Singapore
Economic Factors Affecting Singapore's Outlook
Singapore's economic performance is influenced by a range of factors, including inflation, global market trends, government policies, and technological advancements. These factors shape the overall outlook of the nation and play a significant role in determining future growth potential.
Inflation and Its Impact on Singapore's Economy
Inflation is a crucial economic indicator that affects both businesses and individuals. Rising inflation can erode purchasing power, increase costs, and impact consumer spending. Understanding how inflation may impact Singapore's economy in 2024 is essential for planning and making strategic decisions.
Future Challenges Facing Singapore
While Singapore has enjoyed robust economic growth over the years, it is not immune to challenges. In this section, we will explore some of the key challenges Singapore may face in 2024 and how they might impact its overall outlook.
Demographic Shifts and Aging Population
Singapore's demographic landscape is undergoing significant changes, with an aging population becoming a prominent concern. The challenges associated with an aging population include increased healthcare costs, labor market constraints, and potential strains on social security systems.
Technological Disruptions and Automation
As technological advancements continue to shape the global economy, Singapore must navigate the challenges and opportunities they present. Automation and digitalization can enhance productivity but also pose risks to traditional industries and employment. Adapting to these disruptions is crucial for Singapore's long-term economic sustainability.
Global Trade Dynamics and Protectionism
Singapore, as a global trading hub, is susceptible to changes in global trade dynamics. Rising protectionist sentiments and trade tensions can impact Singapore's export-oriented economy. Analyzing these dynamics and their potential implications is vital to understanding the uncertain outlook in 2024.
Growth Potential in Singapore's Key Industries
Despite the challenges, Singapore possesses significant growth potential in various sectors. In this section, we will explore key industries and sectors that contribute to Singapore's growth and examine the opportunities they present.
Financial Services and Fintech Innovation
Singapore's robust financial services sector has been a key driver of economic growth. In recent years, the rise of fintech has opened up new avenues for innovation and disruption. We will explore the growth potential in this sector and its impact on Singapore's overall outlook.
Biomedical Sciences and Healthcare
Singapore has made significant strides in the biomedical sciences and healthcare sectors. The pursuit of cutting-edge research, world-class medical facilities, and a favorable regulatory environment has positioned Singapore as a regional hub for healthcare innovation. Understanding the growth potential in this sector is crucial for assessing Singapore's future outlook.
Sustainable Energy and Cleantech
In line with global sustainability efforts, Singapore has been actively pursuing sustainable energy solutions and cleantech initiatives. The government's commitment to renewable energy and green technologies presents opportunities for growth and a greener future. We will explore the potential of this sector and its impact on Singapore's economic landscape.
Singapore Outlook amid Inflation - Statistics and Future Trends
Infographics by GO-Globe Singapore
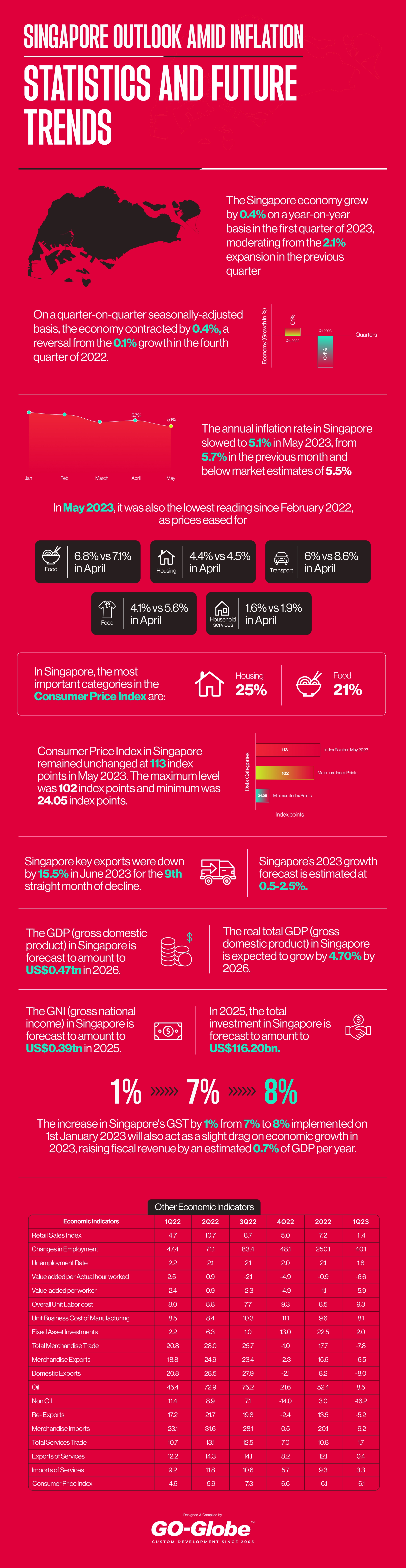
- The Singapore economy grew by 0.4% on a year-on-year basis in the first quarter of 2023, moderating from the 2.1% expansion in the previous quarter
- On a quarter-on-quarter seasonally-adjusted basis, the economy contracted by 0.4%, a reversal from the 0.1% growth in the fourth quarter of 2022.
- The annual inflation rate in Singapore slowed to 5.1% in May 2023, from 5.7% in the previous month and below market estimates of 5.5%
- In May 2023, it was also the lowest reading since February 2022, as prices eased for food (6.8% vs 7.1% in April), housing & utilities (4.4% vs 4.5%), transport (6% vs 8.6%), clothing & footwear (4.1% vs 5.6%), and household durables & services (1.6% vs 1.9%)
- In Singapore, the most important categories in the Consumer Price Index are: Housing (25%) and Food (21%)
- Consumer Price Index in Singapore remained unchanged at 113 index points in May 2023. The maximum level was 102 index points and minimum was 24.05 index points.
- Singapore key exports were down by 15.5% in June 2023 for the ninth straight month of decline.
- Singapore’s 2023 growth forecast is estimated at 0.5-2.5%.
- The GDP (gross domestic product) in Singapore is forecast to amount to US$0.47tn in 2026.
- The real total GDP (gross domestic product) in Singapore is expected to grow by 4.70% by 2026.
- The GNI (gross national income) in Singapore is forecast to amount to US$0.39tn in 2025.
- In 2025, the total investment in Singapore is forecast to amount to US$116.20bn.
- The increase in Singapore's GST by 1% from 7% to 8% implemented on 1st January 2023 will also act as a slight drag on economic growth in 2023, raising fiscal revenue by an estimated 0.7% of GDP per year.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Singapore's uncertain outlook amid inflation, future challenges, and growth potential in 2024 requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors at play. While challenges exist, Singapore's resilience, strategic investments, and commitment to innovation position it for continued growth. By analyzing the economic landscape, potential risks, and growth opportunities, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and adapt to the changing environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the primary drivers of inflation in Singapore?
A: Inflation in Singapore is influenced by various factors, including global oil prices, housing costs, and government policies. Fluctuations in these drivers can impact the overall inflation rate.
Q2: How does an aging population affect Singapore's economy?
A: An aging population poses challenges such as increased healthcare costs, a shrinking labor force, and strains on social security systems. Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining Singapore's economic sustainability.
Q3: How is Singapore adapting to technological disruptions and automation?
A: Singapore is actively investing in technology and digitalization to stay competitive. The government promotes innovation, upskilling, and the adoption of advanced technologies to navigate the challenges of automation.
Q4: What industries contribute significantly to Singapore's economic growth?
A: Singapore's key industries include financial services, biomedical sciences, electronics manufacturing, and logistics. These sectors have been instrumental in driving economic growth and attracting investments.
Q5: How is Singapore promoting sustainable energy solutions?
A: Singapore is actively promoting sustainable energy through initiatives like solar power adoption, electric vehicle incentives, and investment in research and development for clean technologies. These efforts contribute to a greener future and economic growth.
Q6: What are the potential risks to Singapore's growth in 2024?
A: Some potential risks to Singapore's growth include global economic uncertainties, geopolitical tensions, and shifts in trade dynamics. These external factors can impact Singapore's export-oriented economy and overall growth prospects.